94 Which of the Following Are Treatments for Junctional Tachycardia
Lightheadedness dizziness or fainting syncope. Guccione P Di Carlo D Papa M et al.
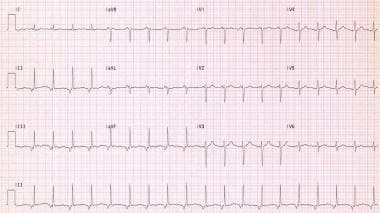
Junctional Rhythm Workup Laboratory Studies Imaging Studies Other Tests
Other symptoms can include.
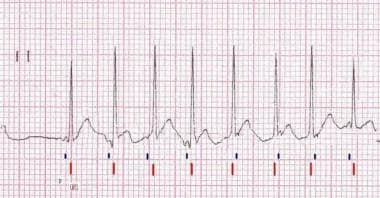
. Fainting syncope Chest pain which may radiate to the back. Complete atrioventricular AV junctional ablation for ventricular rate control in patients with atrial fibrillation 37 patients AV node modification for the treatment of AV node reentrant tachycardia 17 patients accessory pathway ablation 9 patients ablation of the slow zone to cure atrial flutter 4 patients and. When is the identification of the specific dysrhythmia important in terms of treatment of the patient.
Doses and alternatives are similar to management of bradycardia in general. Identify the following rhythm. The normal inherent rate of the AV junction is.
This tachycardia usually is managed by withholding digoxin and administering potassium. Congenital junctional ectopic tachycardia JET is usually initially treated with antiarrhythmic therapy with the choice of medication guided by the degree of coexisting ventricular dysfunction. -It has a narrow QRS.
Lidocaine phenytoin and digoxin-specific antigen-binding fragments also may be used. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. Symptomatic junctional rhythm is treated with atropine.
In babies junctional tachycardia may be as fast as 250-350 beats per minute. Junctional ectopic tachycardia JET often occurs in the early postoperative period following surgery for congenital heart diseases and may lead to hemodynamic compromise. It is irregular in a pattern of grouped beating.
Junctional ectopic tachycardia JET is a serious heart rhythm disturbance affecting 1480 of all infants and children undergoing surgery for a congenital heart defect 13The absence of synchronised atrial activity in combination with postoperative ventricular dysfunction may significantly decrease cardiac output and is associated with increased morbidity and. What type of heart rate is characteristic of a patient who has junctional escape rhythm. Junctional rhythm Figures 8-10 8-11 8-12 and 8-13 and Box 8-2 is an arrhythmia originating in the AV junction with a rate between 40 and 60 beats per minute.
-It has inverted P waves. Prophylactic amiodarone reduces junctional ectopic tachycardia after tetralogy of Fallot repair. When you record the ECG the tracing shows that the P waves follow the QRS complexes and that the distance from each P wave to the next R wave is 06 seconds.
Your training and place of employment. Ergul Y Ozturk E Ozgur S Ozyurt A Cilsal E Guzeltas A. Postoperative arrhythmias occur frequently in the early postoperative period following cardiac surgery in children.
The effect of junctional tachycardia on the patient depends on. Analysis of data from 22 institutions reporting 99 cases of JET and 5 cases of accelerated junction rhythm reported an efficacy of 60 6. Your heart rate may be above 100 beats per minute or more.
What is the difference between accelerated junctional rhythm and junctional tachycardia. Ivabradine is an effective antiarrhythmic therapy for congenital junctional ectopic tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy during infancy. If the junctional rhythm is due to digitalis toxicity then atropine digoxin immune Fab Digibind or both may be necessary.
Objectives To determine the outcomes of medical management pacing and catheter ablation for the treatment of nonpost-operative junctional ectopic tachycardia JET in a pediatric population. In refractory cases of. Treatment for junctional tachycardia might include with holding digitalis administration.
Junctional rhythm can occur under either of the following conditions. Which of the following is NOT true about Junctional Tachycardia. Junctional rhythm is the normal rhythm of the AV junction.
An enhanced junctional impulse may override the SA node and produce either an accelerated junctional rhythm rate 60100 bpm or a junctional tachycardia with rates greater than 100 bpm. Junctional tachycardia is caused by abnormal automaticity in the atrioventricular node cells near the atrioventricular node or cells in the bundle of His. -It is a very rapid rhythm.
Patients underwent one of the following catheter ablation procedures. The most common symptom of junctional tachycardia is a fast heart rate. Your role regarding evaluation of the rhythm strip and assessment of the patient will.
_____ may be used to terminate junctional tachycardia rhythm. A patient has an accelerated junctional rhythm. What is the PR interval.
Combined infusion of flecainide and amiodarone has been used in a refractory case of post operative JET 18. Tachyarrhythmias originating in the atrioventricular AV node and AV junction including the bundle of His complex BH are called junctional tachycardia JT or junctional ectopic tachycardia JET1 2 3 AV junction refers to the AVspecialized conducting system consisting of the transitional cell zone the AV node and its extensions and the. With junctional tachycardia electricity is fired from a source very close to the AV node at a very fast rate.
Hypothermia treatment of junctional ectopic tachycardia after surgical repair of congenital heart defects. Amiodarone is also effective in non-post operative JET. Automatic AV junctional tachycardia also known particularly in pediatrics as junctional ectopic tachycardia primarily affects chldren and infants.
Which of the following treatments may be needed to. Treatment of junctional beats and rhythm. Press gently on your eyes while theyre closed.
Accelerated junctional rhythm or junctional tachycardia can occur with inferior myocardial infarction or dioxin toxicity. Junctional ectopic tachycardia JET is one of the more commonly encountered arrhythmia with an overall incidence estimated between 36 and 108 with two case series reporting incidence as high as 12 and 27 respectively12345678. Heart Rhythm Disorders in Children Pediatric Nonpost-Operative Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia Medical Management and Interventional Therapies.
-It is irregular in a pattern of grouped beating. The rate of the rhythm. It often is incessant.
Its exact etiology is unknown however longer cardiopulmonary bypass CPB time aortic cross clamp ACC time catecholamines and hypomagnesemia are known risk factors. Junctional tachycardia is a specific type of tachycardia that involves the specialized conducting tissue in and around the AV node and its associated structures. This is gentle pressure on your neck where the carotid artery splits into two branches.

Junctional Ectopic Tachycardia Workup Laboratory Studies Electrocardiography Imaging Studies

Accelerated Av Junctional Rhythm 75 Bpm With Right Bundle Branch Block Download Scientific Diagram
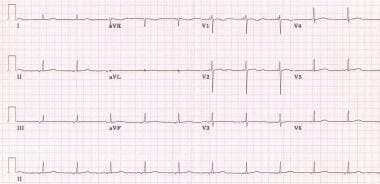
Junctional Rhythm Workup Laboratory Studies Imaging Studies Other Tests
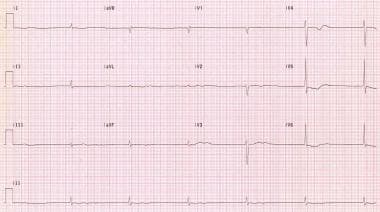
Junctional Rhythm Workup Laboratory Studies Imaging Studies Other Tests
No comments for "94 Which of the Following Are Treatments for Junctional Tachycardia"
Post a Comment